Efficient inventory management is a huge liability for fast-growing businesses. Trying to keep tabs on your stock while juggling multiple sales channels and warehouses demands precise oversight and can significantly impact cash flow, operational efficiency, and customer satisfaction if mismanaged.
This is where a perpetual inventory system can help. A perpetual inventory system offers real-time stock tracking and financial reporting through electronic records. It shows exactly what stock you have, its location, and when to restock without manual counting.
This powerful system optimizes operations by simplifying SKU management based on sales data, spotting lost inventory and missed transactions, and reducing labor costs.
The result? You make smarter purchasing decisions that improve inventory turnover, reduce carrying costs, and ultimately increase profitability while ensuring products remain in stock to satisfy customers.
Let’s learn about perpetual inventory systems, how they work, their benefits, and why they’re needed for businesses to stay competitive today.
What Is a Perpetual Inventory System?
A perpetual inventory system is a computerized method that continuously tracks and updates inventory levels in real time, thus eliminating the need for manual counting. It uses integrated software, barcode scanners, and point-of-sale systems to provide accurate, up-to-the-minute stock information.
The system seamlessly integrates with point-of-sale (POS) and warehouse management software, allowing efficient data flow across business operations. As items are scanned, the inventory count is instantly updated in the central database.
This system differs from perpetual inventory (the accounting method) in that the perpetual inventory system refers to the technological infrastructure that helps with real-time tracking.
Unlike periodic inventory systems that rely on manual counts, perpetual systems automatically record every transaction as it happens, removing the need for frequent physical counts and maintaining precise inventory records.
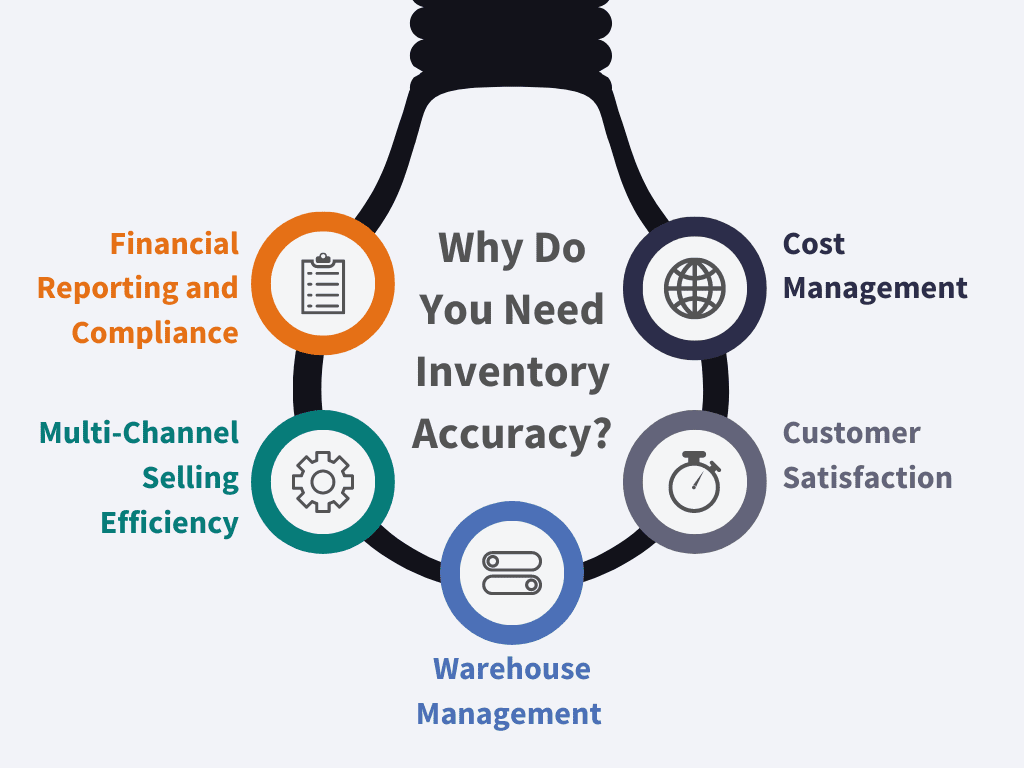
The Importance of Inventory Accuracy
A recent survey found that 40% of retailers cancel at least one in ten customer orders because of errors in inventory data. That’s 10% of potential revenues gone because of inventory accuracy.
Let’s understand in detail why inventory accuracy is crucial for your business growth:
Financial Reporting and Compliance – Accurate inventory records ensure proper inventory asset representation on balance sheets, enabling correct COGS calculation. This reflects true financial health, meeting accounting standards and tax regulations.
Multi-Channel Selling Efficiency – For fast-growing businesses selling across multiple platforms, real-time inventory updates across platforms prevent overselling, reducing stockouts and backorders.
Warehouse Management – Consolidated view of inventory data across locations enables efficient transfers and optimal distribution, reducing unnecessary movements and costs.
Customer Satisfaction – Ensuring product availability improves order fulfillment, reducing cancellations and delays. Consistent delivery builds trust and loyalty.
Cost Management – Avoiding excess inventory saves storage costs and frees up capital. Accurate inventory minimizes stockouts, preventing lost sales and rush reordering expenses.
How Does It Work: A Step-By-Step Guide
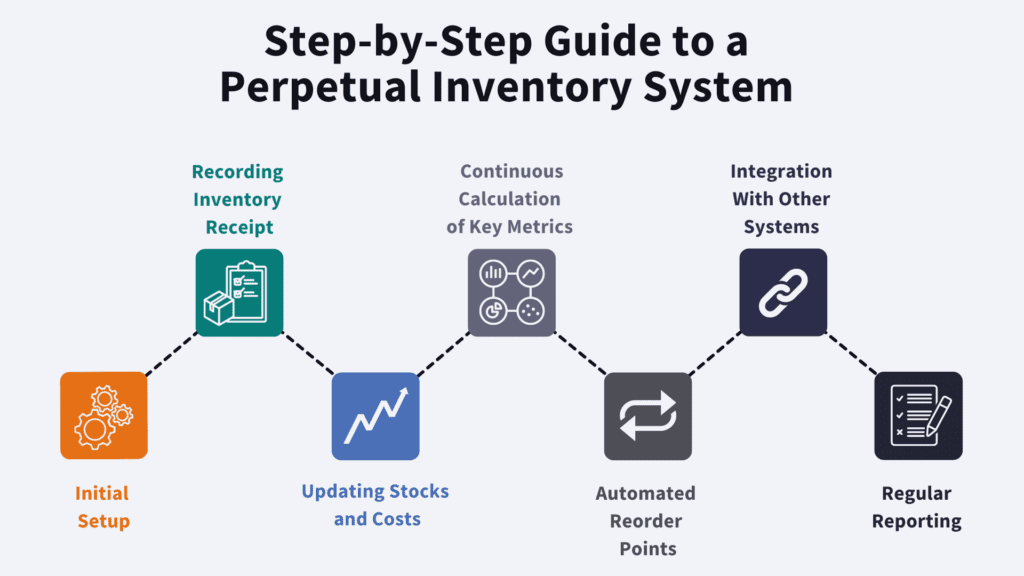
Let’s understand how the perpetual inventory system works in more detail. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Initial Setup – The process starts when you enter all current inventory into the system with detailed information such as quantity, cost, location, and other relevant data like SKUs or barcodes.
Recording Inventory Receipt – When new inventory arrives, it’s immediately recorded in the system. This includes scanning barcodes or entering data manually. The system automatically updates stock levels and recalculates the unit cost of inventory items based on new additions.
Updating Stocks and Costs – As sales occur, the system automatically deducts sold items from the inventory count. This real-time update ensures that stock levels are always accurate. Simultaneously, the system records the transaction, updating financial data such as revenue and cost of goods sold (COGS).
Continuous Calculation of Key Metrics – A perpetual inventory system can continuously calculate and update important metrics, including COGS, gross profit, and inventory turnover ratios. These real-time calculations provide an always-current view of your business’s financial health.
Automated Reorder Points – The system can automatically adjust reorder points based on historical data and predefined rules. When inventory for a particular item reaches this threshold, the system can generate purchase orders automatically, helping with optimal stock levels.
Integration with Other Systems – Perpetual inventory systems often integrate with other business systems, such as warehouse management systems, point-of-sale (POS) terminals, and accounting software. This integration helps with seamless data flow across different aspects of the business.
Regular Reporting – The system generates automated reports on various aspects of inventory management, thus giving insights into inventory status, sales trends, slow-moving items, and other relevant data, helping with informed decision-making.
Perpetual Inventory System Example
A clothing retailer uses perpetual inventory across multiple stores. When a shirt is sold, scanning updates the inventory instantly. The system auto-generates reorder requests at preset thresholds.
Managers access real-time reports on stock levels, bestsellers, and slow movers for all locations, aiding decisions on redistribution, reordering, and promotions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Perpetual Inventory System

A perpetual inventory system can help your fast-growing business run smoothly in several ways. Here are some examples:
- Reduces stockouts and overstocks – Provides real-time visibility into stock levels.
- Improves inventory accuracy – Reduces human inventory counting and data entry errors, leading to more accurate inventory records.
- Decreases labor costs – Automates many inventory management tasks and reduces the need for manual stocktaking.
- Enhances decision-making – Real-time data allows for better choices regarding purchasing, pricing, and sales strategies.
- Increases customer satisfaction – Improved inventory accuracy ensures product availability and meets customer expectations.
- Improves multi-channel coordination – Enables better synchronization between different business locations and sales platforms.
However, there are some setbacks to a perpetual inventory system:
- Requires significant investment – Implementing a perpetual inventory system can be costly, demanding software, hardware, and staff training.
- Risks operational disruptions – System failures or data corruption could temporarily halt inventory tracking.
- Necessitates periodic checks – Despite real-time tracking, discrepancies can still occur due to theft or damage, requiring occasional physical counts.
- Introduces error potential – Doesn’t account for scanning errors (duplicate/missed scans), software malfunctions, or employee mistakes, which can affect inventory accuracy.
- Increases cybersecurity needs – Reliance on system updates creates hacking risks, necessitating enhanced cybersecurity measures.
When to Use a Perpetual Inventory System
Companies that should use this system are those with multiple locations, higher sales volumes, or multiple inventory streams.
For businesses handling high-value items, perpetual inventory systems offer real-time tracking for close monitoring of expensive items, reducing theft risks.
For perishable items, managing stock rotation and expiration dates becomes easier, minimizing waste and ensuring product quality.
Formulas Used to Calculate Perpetual Inventory
When manually calculating perpetual inventory (the accounting method), here are the accounting formulas you can use.
Basic Perpetual Inventory Formula
This is the fundamental formula for perpetual inventory:
| Beginning Inventory + Purchases – Cost of Goods Sold = Ending Inventory |
This formula is continuously updated as transactions occur, providing a real-time view of your inventory balance. You can use it when you need to quickly assess current stock quantities or generate up-to-date financial statements.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
COGS is calculated in real-time using the formula below. This method updates companies on their inventory costs:
| COGS = Beginning Inventory + Purchases – Ending Inventory |
Average Cost Method
Many perpetual inventory systems use the average cost method to value inventory:
| Average Cost Per Unit = Total Cost of Goods / Number of Units |
This method helps allocate costs evenly across all items, simplifying inventory valuation and COGS calculations.
It’s best used by businesses with similar inventory items to simplify accounting for large volumes of similar products.
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
The EOQ formula is used to measure the optimal order quantity:
| EOQ = √(2DS/H) |
“D” indicates annual demand, “S” indicates order cost, and “H” indicates holding cost per unit per year.
With this formula, inventory costs can be minimized by balancing order and holding costs. However, use this only when demand and costs are relatively stable.
Reorder Point
To maintain optimal stock levels, perpetual inventory systems often calculate reorder points:
| Reorder Point = (Average Daily Usage x Lead Time) + Safety Stock |
This formula ensures new orders are placed at the right time to avoid stockouts.
Use this method to maintain optimal inventory levels of critical items (whose absence can halt the production or supply chain) when lead times are consistent and predictable.
Tips for Improving Your Inventory Management Processes

While understanding the calculations is important, there are some ways to figure out how to best manage inventory.
- Regularly match system data with physical inventory counts to ensure accuracy.
- Use cycle counting procedures to verify inventory accuracy without disrupting daily operations.
- Aim for improved accuracy in inventory cycle counts. For example, Ware2Go maintains an SLA of 99.9% accurate inventory cycle counts.
- Use a system like Ware2Go’s reporting features (for inventory fluctuations, such as the quantity of goods on hand at the SKU level) to analyze sales trends, identify slow-moving items, and optimize stock levels.
- Integrate the perpetual inventory system with other business systems, like accounting and customer relationship management, for a more holistic view of operations.
- Train staff on new practices and how to use the perpetual inventory system.
Differences Between Periodic and Perpetual Inventory Systems
| Periodic Inventory System | Perpetual Inventory System | |
| Frequency of Updates | At specific intervals | Continuously |
| Inventory Data | Accurate only after physical count | Real time |
| Implementation Cost | Typically less expensive | Generally more expensive |
| Labor Requirements | More manual labor for counts | Less manual labor for counts |
| Inventory Control | Limited | Better |
| Decision-Making Capabilities | Limited | Enhanced due to real-time data |
| Suitability | Small businesses with limited inventory | Larger operations or complex inventory needs |
Periodic and perpetual inventory systems differ in their approach to stock management. Periodic systems use physical counts at set times, offering accurate data only after these counts. They’re cheaper to set up but need more manual work (thus costing more in terms of labor and time needed) and are suitable for businesses with limited inventory.
On the other hand, perpetual systems constantly update inventory levels, providing real-time data. This ongoing tracking allows for better inventory control and smarter decision-making. Larger operations or those with complex stock needs often require the real-time accuracy of a perpetual system.
Perpetual Inventory in Multi-Channel, Multi-Warehouse Environments
Perpetual inventory systems help in multi-channel, multi-warehouse environments by providing real-time visibility across the entire network. This lets businesses treat their dispersed inventory as a unified pool, helping with more strategic allocation decisions.
Instead of each location operating in isolation, the system gives a holistic view that supports swift stock movement and timely demand fulfillment.
With this interconnected approach, businesses can optimize inventory levels across channels and locations. It becomes possible to quickly spot and resolve imbalances—shifting stock from overstocked locations to those facing potential stockouts.
This continuous reallocation increases inventory efficiency and improves the ability to meet customer demand across all sales channels.
Supplementing Perpetual Inventory with Cycle Counts
Remember, while perpetual inventory systems provide real-time digital tracking, they can’t account for discrepancies caused by theft, damage, or human error (for example, an employee in a grocery store accidentally not scanning an item).
Regular physical checks or cycle counts help verify the accuracy of digital records and maintain the integrity of the inventory system.
Cycle counting involves regularly counting a small portion of the inventory on a rotating basis.
Here’s how it works:
- Select a subset of items to count.
- Physically count these items.
- Compare the count to system records.
- Investigate and correct any discrepancies.
- Repeat the process with different items.
By combining perpetual inventory systems with cycle counts, you can maintain highly accurate inventory records while avoiding the cost of counting the whole inventory in one go.
FAQs
Let’s tackle some common questions here:
What Is an Example of a Perpetual Inventory System?
A retail store using barcode scanners and an integrated database to update stock levels instantly with each sale/purchase.
What Is a Perpetual and Continuous Inventory System?
A method that tracks inventory in real time, constantly updating stock levels as transactions occur, without the need for periodic manual counts.
How Does a Perpetual Inventory Control System Improve Accuracy?
A perpetual inventory system records all transactions instantly, reducing errors and providing real-time data. It allows immediate stock verification, automated reordering, and quick inconsistency detection, improving inventory management and financial reporting accuracy.
Taking the Next Step: Implementing Your Perpetual Inventory System
Adopting a perpetual inventory system is a big step that can really pay off. It offers accurate stock and sales data, optimizing orders, reducing costs, and preventing stockouts. This can improve cash flow and customer satisfaction.
But even the best system needs a human touch. So, regular cycle counts must be an important part of your inventory management strategy.
To streamline your inventory management system, consider partnering with experts like Ware2Go. Our 99.9% inventory cycle count accuracy and streamlined processes can help make the most of your perpetual inventory system. Contact us today!





